Beware of Bogus Adobe Reader Installers Spreading Malware
Jeff Wolverton

In the constantly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, vigilance is paramount. A new and sophisticated threat has emerged, where cybercriminals cunningly use fake Adobe Acrobat Reader installers to disseminate a complex malware known as Byakugan.
The Deceptive Start:
The ploy begins with a PDF file, typically in Portuguese, which displays a blurred image. It prompts the viewer to download Adobe Reader to view the content clearly. However, this is a trap leading to a malicious journey.
The Discovery and Initial Reports:
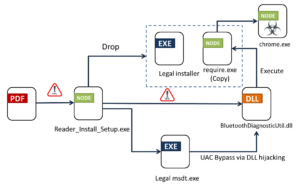
This intricate attack mechanism was first brought to light by the AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) and subsequently analyzed by Fortinet FortiGuard Labs. It was revealed that the infection commences once the victim is enticed into clicking a link within the PDF. This action downloads an installer named “Reader_Install_Setup.exe,” marking the start of the malware’s invasion.
Infection Tactics and Payload:
The Byakugan malware showcases its complexity by employing tactics like DLL hijacking and bypassing Windows User Access Control (UAC). It introduces a malicious DLL, “BluetoothDiagnosticUtil.dll,” which triggers the release of the main malware payload. Intriguingly, the malware also installs a legitimate PDF reader, which adds a layer of deception.
Technical Insights and Capabilities:
Diving deeper, security researcher Pei Han Liao elaborates that Byakugan is based on node.js and is packed with multiple functionalities. The malware’s capabilities range from gathering system information and desktop surveillance using OBS Studio to capturing screenshots, downloading cryptocurrency miners, keystroke logging, and data theft.
Emerging Trends and Challenges in Detection:
Fortinet highlights an emerging trend in the malware development landscape: blending legitimate and malicious components. This strategy significantly complicates detection and analysis, posing a substantial challenge to cybersecurity experts.
Broader Context and Additional Threats:
Furthermore, this blog discusses ASEC’s recent uncovering of the Rhadamanthys information stealer and the misuse of Notepad++ in the distribution of the WikiLoader malware. These instances underscore the dynamic and ever-changing nature of cyber threats.
Conclusion:
The discovery of the Byakugan malware campaign serves as a stark reminder of the necessity for heightened awareness and robust cybersecurity measures. It’s crucial for users to exercise caution when downloading software and to stay informed about the latest developments in cyber threats.
Call to Action:
Stay vigilant and informed. Reach out to us at PivIT Strategy to get a full understanding of this threat and how to protect yourself.
Jeff Wolverton
Jeff, the CEO of PivIT Strategy, brings over 30 years of IT and cybersecurity experience to the company. He began his career as a programmer and worked his way up to the role of CIO at a Fortune 500 company before founding PivIT Strategy.