Fake CAPTCHA Malware: Familiar Tools to Deceive Users
Jeff Wolverton

Cybersecurity threats are growing in both complexity and frequency, it’s essential for users to stay vigilant. One increasingly popular tactic among cybercriminals is exploiting fake CAPTCHA pages. What appears to be a typical CAPTCHA challenge—like clicking “I am not a robot” or “Verify you are human”—often hides a much darker agenda. These fraudulent CAPTCHA pages can deceive users into downloading and executing malware, compromising personal data, and exposing organizations to costly breaches.
What Is Fake CAPTCHA Malware?
At its core, fake CAPTCHA malware is a deceptive scheme in which a malicious CAPTCHA page prompts users to perform what seems like an innocuous action, like confirming they’re human. Instead of simply validating access, however, these malicious CAPTCHA pages are rigged with scripts designed to download and execute malware. This form of social engineering preys on the user’s trust in CAPTCHA as a security measure.
Fake CAPTCHA pages are usually presented in pop-ups or embedded within illegitimate websites. Upon clicking, users unknowingly initiate the download of malicious code, which may result in anything from ransomware infections to credential theft.
How Fake CAPTCHA Malware Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The attack structure of fake CAPTCHA malware becomes clearer when we look at real-world examples. Below are two visuals that illustrate how cybercriminals use deceptive CAPTCHA prompts to lead unsuspecting users into executing harmful scripts.
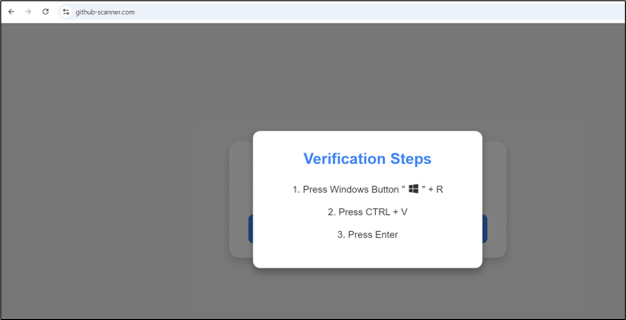
Image 1: A Deceptive CAPTCHA Verification Prompt
In this example, the CAPTCHA page resembles a typical verification prompt. It instructs users to press the Windows button along with “R” to open the Run command, then paste a copied script and press Enter. This sequence is unusual for a legitimate CAPTCHA but is intended to make users execute a malicious PowerShell command.
Key points:
- Unexpected Instructions: Instead of validating identity through normal means, it asks for keyboard commands that open a system function. This should be a red flag for users.
- PowerShell Vulnerability: By pasting a script directly into the Run prompt, users unknowingly grant attackers the ability to run malicious scripts on their system.
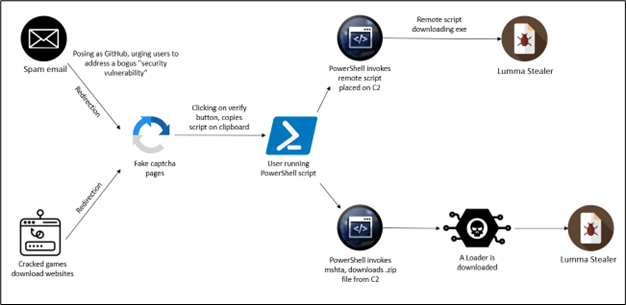
Image 2: Attack Flow of Fake CAPTCHA Malware
This diagram illustrates the complete flow of a fake CAPTCHA malware attack, showing how it begins with a deceptive prompt and escalates to malware installation.
Steps:
- Initial Contact: The attack may start from various points, including spam emails or cracked software sites that direct users to the fake CAPTCHA page.
- Script Execution: When users comply with the fake CAPTCHA’s instructions, a malicious PowerShell script runs, downloading additional malware from a command-and-control (C2) server.
- Malware Deployment: The script invokes further processes, including downloading loaders or direct malware like the Lumma Stealer, which compromises system security and enables data theft.
This visual breakdown highlights the importance of recognizing phishing tactics and understanding that legitimate CAPTCHA pages will never ask users to execute commands outside of the browser environment.
Why Are Fake CAPTCHA Pages So Effective?
- Familiarity Breeds Trust: CAPTCHA tests have become a universally recognized security feature. When users encounter one, they are conditioned to trust it and proceed without hesitation.
- Highly Targeted Pop-Ups: Cybercriminals often place fake CAPTCHA pages on sites where users expect validation processes, such as login screens or payment portals, making the deception even more believable.
- Stealthy Execution of Malware: Once a user clicks “Verify” or “I am not a robot,” the malware is often downloaded instantly, with no visible clues to alert the user. The malware may operate in the background, collecting data or exploiting vulnerabilities.
The Impact of Fake CAPTCHA Malware on Organizations
For businesses, this form of malware is particularly dangerous. Malware embedded in fake CAPTCHA pages can easily spread through corporate networks, leading to data breaches, unauthorized access, and damage to reputation. Worse, if an employee unknowingly downloads malicious code on a company device, it can compromise sensitive customer data or intellectual property.
According to cybersecurity organizations like the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), awareness and early detection are critical in combating this threat. Once deployed, malware from fake CAPTCHA attacks can be challenging to remove, making preventive measures essential.
How to Spot and Avoid Fake CAPTCHA Pages
- Examine the URL Carefully: Avoid entering sensitive information or clicking CAPTCHAs on unfamiliar websites. Legitimate CAPTCHAs are typically hosted on reputable sites.
- Verify Unexpected Pop-Ups: If a CAPTCHA unexpectedly appears, close the pop-up and avoid engaging with it. If a site repeatedly prompts CAPTCHA tests, this could signal a phishing attempt.
- Use Advanced Security Software: Up-to-date security software can detect and prevent malware. Tools that scan for unusual browser behavior or script execution are particularly effective in blocking these deceptive tactics.
- Educate and Train Employees: Organizations should offer training on the dangers of fake CAPTCHA malware, as awareness is a powerful line of defense.
Steps Businesses Can Take to Protect Against Fake CAPTCHA Malware
- Implement Endpoint Security Solutions: Comprehensive endpoint protection can help detect malicious downloads initiated by fake CAPTCHAs.
- Integrate Email and Web Filtering Tools: Many fake CAPTCHA pages are distributed via phishing emails. Filtering software can block these emails before they reach employees.
- Conduct Routine Security Awareness Training: Employees should understand how to identify phishing attempts, fake CAPTCHA pages, and other social engineering tactics.
- Partner with Trusted Cybersecurity Providers: A managed cybersecurity provider like PivIT Strategy can monitor network activity, detect unusual behavior, and help prevent malware from infecting your systems.
Conclusion
Fake CAPTCHA pages are a sobering reminder that attackers continually evolve their methods to exploit user trust. With their effectiveness rooted in social engineering, fake CAPTCHA malware can easily trick users into unknowingly compromising their devices or networks. By maintaining awareness, educating employees, and investing in robust security measures, businesses can reduce their vulnerability to this increasingly common cyber threat.
For more information on defending against fake CAPTCHA malware and other cybersecurity threats, contact PivIT Strategy to see how we can support your organization’s security strategy.
Jeff Wolverton
Jeff, the CEO of PivIT Strategy, brings over 30 years of IT and cybersecurity experience to the company. He began his career as a programmer and worked his way up to the role of CIO at a Fortune 500 company before founding PivIT Strategy.
