FrigidStealer Malware Targets MacOS: Exploits Browser Updates
Mitch Wolverton
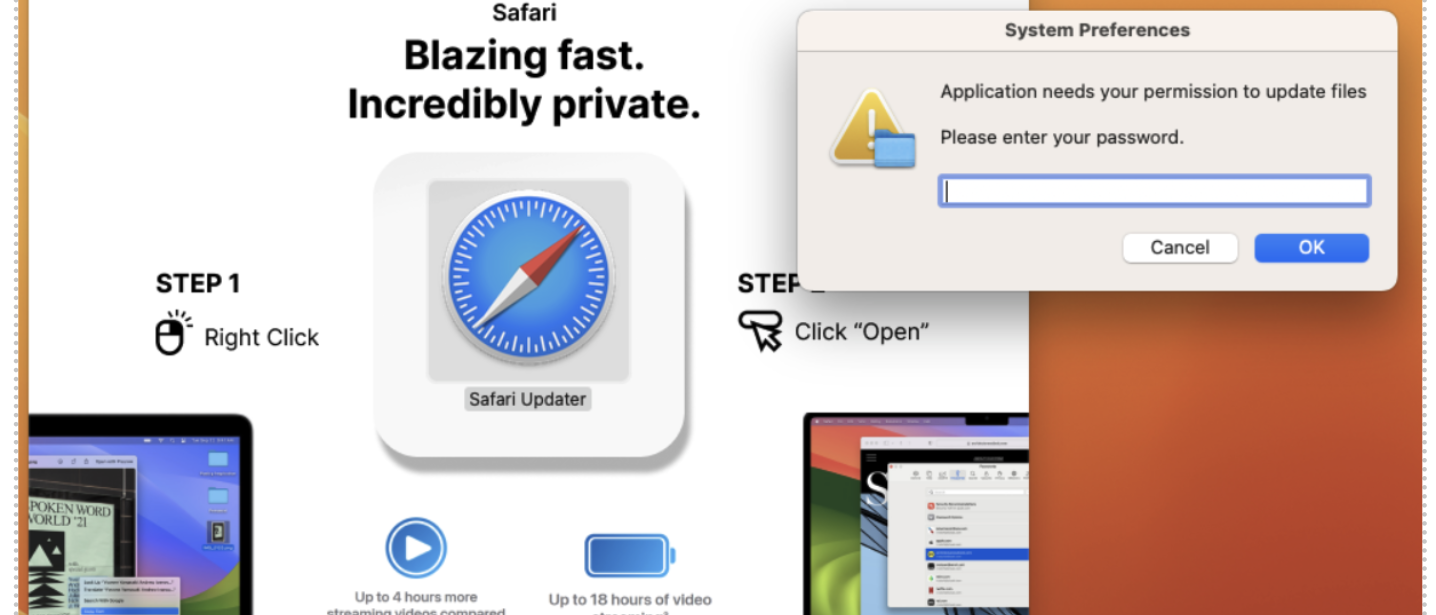
Cybercriminals are setting their sights on macOS users with a newly discovered malware known as FrigidStealer. Disguised as a fake browser update, this sophisticated information-stealing malware is part of a broader cyberattack campaign orchestrated by a threat actor identified as TA2727.
The Emergence of FrigidStealer
Security researchers have uncovered that FrigidStealer is being distributed through compromised websites using malicious JavaScript injects. These fake browser updates mimic legitimate installers for Google Chrome or Safari, tricking unsuspecting users into downloading malware. Once installed, FrigidStealer can extract sensitive files, browser data, Apple Notes, and cryptocurrency-related information.
How FrigidStealer Works

FrigidStealer operates similarly to other macOS-focused information stealers. To bypass Apple’s Gatekeeper protections, users must manually launch the unsigned application. Once executed, the malware:
- Runs a Mach-O executable to install itself.
- Uses WailsIO, a development framework that renders content in the user’s browser, adding an extra layer of deception.
- Prompts the user via AppleScript to enter their system password, granting it elevated privileges.
- Collects and exfiltrates sensitive information from the device.

Why MacOS Users Are Being Targeted
For years, macOS has been viewed as a more secure operating system compared to Windows. However, cybercriminals are adapting their techniques to exploit the increasing number of macOS users. The growing popularity of macOS devices in professional environments makes them an attractive target for financially motivated cybercriminals.
FrigidStealer is particularly dangerous because it blends social engineering with technical exploits. Unlike traditional malware that often requires deep technical knowledge to execute, this malware relies on tricking users into clicking what appears to be a legitimate browser update. This method capitalizes on user trust, making it highly effective.
The Threat Actors Behind the Attack
TA2727 is not operating alone. Security reports indicate that this financially motivated group is working alongside TA2726 and TA569, both of which specialize in distributing malware through traffic distribution systems (TDS) and JavaScript-based loaders. These groups have been active since at least September 2022, leveraging compromised websites to spread malware across multiple operating systems.
Cross-Platform Threats
The FrigidStealer campaign is part of a multi-platform attack strategy:
- Windows users are targeted with Lumma Stealer or DeerStealer, often through MSI installers.
- Android users are redirected to Marcher, a banking trojan that has plagued mobile users for over a decade.
- MacOS users, particularly those outside North America, are now at risk from FrigidStealer via fake update redirects.
Financial Motives Behind FrigidStealer
The primary goal of these cybercriminals is financial gain. Information stealers like FrigidStealer collect browser data, login credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, and personal information, all of which can be monetized on underground forums or dark web marketplaces. Stolen credentials can also facilitate further attacks such as identity theft, corporate espionage, or ransomware deployment.
The Growing Threat of MacOS Malware
MacOS has long been perceived as a less common target for cybercriminals compared to Windows. However, recent campaigns indicate that attackers are increasingly developing macOS-specific threats. The use of fake browser updates as a malware delivery method has proven effective, as seen in other campaigns distributing SocGholish (FakeUpdates) and other loaders.
Security analysts are also tracking the rise of new information stealers like Astral Stealer and Flesh Stealer, both designed to evade detection and persist on compromised systems. Flesh Stealer, in particular, demonstrates advanced anti-analysis techniques, avoiding execution in virtual machine (VM) environments to prevent forensic analysis.
The Evolution of Social Engineering in Cyber Attacks
FrigidStealer is another example of how cybercriminals are evolving their methods. Instead of relying solely on traditional phishing emails, attackers are now using compromised websites to inject malicious JavaScript. This tactic makes it harder for traditional security measures, such as email filters, to detect and block the threat.
By using geographically targeted payloads, cybercriminals can further evade detection. If a website visitor is identified as using Windows, they receive Windows-based malware. If the visitor is on macOS, they are redirected to download FrigidStealer. This tailored approach ensures a higher success rate for malware infections.
How to Protect Against FrigidStealer Malware and Similar Threats
To safeguard against FrigidStealer and similar macOS malware threats, users should:
- Avoid downloading software from pop-ups or unfamiliar websites. Always install browser updates from official sources.
- Verify digital signatures before running applications on macOS.
- Enable Gatekeeper and XProtect, Apple’s built-in security features that help block unauthorized applications.
- Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to monitor and mitigate emerging threats.
- Stay updated on threat intelligence from cybersecurity providers to remain aware of new attack vectors.
Steps for Businesses to Mitigate Risk
For businesses using macOS in their environments, additional cybersecurity strategies should be implemented:
- Deploy endpoint security solutions tailored for macOS to detect and block threats.
- Educate employees on social engineering tactics used in malware campaigns.
- Regularly monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Establish a zero-trust security framework to reduce attack surfaces.
Conclusion
The emergence of FrigidStealer Malware is a stark reminder that macOS is no longer immune to sophisticated cyber threats. Fake browser updates continue to be a favored method for distributing malware, and as cybercriminals refine their tactics, both individuals and enterprises must remain vigilant. Organizations should implement robust cybersecurity measures, including regular security training, threat monitoring, and proactive response strategies to mitigate the risk of malware infections.
For businesses looking to fortify their security posture, PivIT Strategy offers tailored cybersecurity solutions designed to detect and prevent evolving threats like FrigidStealer. Contact our team today to strengthen your defenses against macOS malware and beyond.
Mitch Wolverton
Mitch, Marketing Manager at PivIT Strategy, brings over many years of marketing and content creation experience to the company. He began his career as a content writer and strategist, honing his skills on some of the industry’s largest websites, before advancing to specialize in SEO and digital marketing at PivIT Strategy.
