Understanding Malvertising: A Hidden Threat in Digital Advertising
In the vast world of digital marketing, a sinister form of attack has emerged, blending into the everyday barrage of online advertisements. This threat, known as “malvertising” (“malicious advertising”), involves the use of online advertising as a vehicle to distribute malware. Unlike other cyber threats, malvertising leverages the essential nature of digital ads to infiltrate computers and networks, making it a particularly stealthy and dangerous form of cyber-attack. This blog explores what malvertising is, how it works, its implications, and the steps individuals and organizations can take to protect themselves.
What is Malvertising?
Malvertising involves injecting malicious code into legitimate online advertising networks and webpages. The ads look no different from typical advertisements, but they harbor hidden malware designed to execute when someone clicks on them, or sometimes even if they simply load on a user’s browser. This method of attack can lead to unintended downloads of malware, ransomware infections, or the exploitation of vulnerabilities within a system—all without the user’s knowledge.
How Does Malvertising Work?
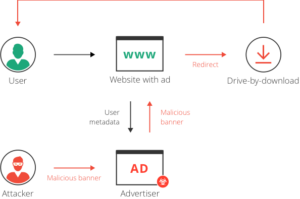
The process typically begins when an attacker creates an ad containing malicious code. This ad is then submitted to advertising networks, which distribute the ads across various websites. The complexity and automation of the digital advertising ecosystem allow these malicious ads to slip through checks, often by mimicking the behavior of legitimate ads until they reach the target’s device.
Victims of malvertising might encounter these ads on any site—even those considered highly reputable. This is because malvertising exploits the trust users have in well-known sites that display ads from external networks. Once an infected ad is displayed, the malware can be triggered by various actions, such as clicking the ad or hovering over it, or it may run automatically in the background.
Types of Attacks Launched Through Malvertising
- Drive-by Downloads: Simply visiting a site with malicious ads can result in malware being downloaded and installed without user interaction.
- Ransomware: Malvertising can be used to lock a user’s device or encrypt their files until a ransom is paid.
- Spyware: It can also introduce spyware, allowing attackers to spy on the victim’s online activities and steal sensitive information.
- Exploit Kits: These are tools used to exploit known vulnerabilities in browsers and other software. Malvertising often redirects users to sites that host these kits.
Implications of Malvertising
The implications of malvertising are extensive, affecting users, businesses, and the integrity of the online advertising industry. For users, the impact ranges from annoying disruptions to severe privacy breaches and financial loss. Businesses, on the other hand, face damage to reputation, loss of consumer trust, and potential legal consequences.
Moreover, malvertising undermines the economic foundation of the free internet, which relies heavily on advertising revenue. When users start fearing that ads could be a source of malware, they might resort to ad blockers, which can decrease revenue for sites that depend on ads.
Protecting Against Malvertising
Protecting against malvertising requires a multi-layered approach, involving both individuals and businesses:
- Regular Updates: Keep all software, especially browsers, up-to-date to mitigate the risk of exploit kits targeting known vulnerabilities.
- Use of Ad Blockers: Installing ad blockers can prevent malicious ads from loading. However, this is a double-edged sword, as it also affects legitimate sites that rely on ad revenue.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Businesses should use reputable ad networks and regularly audit their digital ad supply chain. Employing services that scan for and block malicious ads can also be beneficial.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding the signs of malvertising and being cautious with online ads can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to such attacks.
Conclusion
Malvertising represents a sophisticated and hidden danger in the digital age, capitalizing on the complexities of the online advertising ecosystem. By understanding how malvertising works and taking proactive steps to protect themselves, both individuals and businesses can significantly mitigate the risks associated with this deceptive form of cyber threat. As we move forward, the role of cybersecurity in digital advertising will become more crucial in ensuring the safety and integrity of our online experiences.